Lotus (=Acmispon) salsuginosus, Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil




Scientific Name: Lotus salsuginosus (Acmispon maritimus)
Common Name: Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil
Also Called: Humble Trefoil, Maresfat
Family: Fabaceae or Leguminosae Family
Synonyms: (Acmispon maritimus)
Status: Native
Duration: Annual
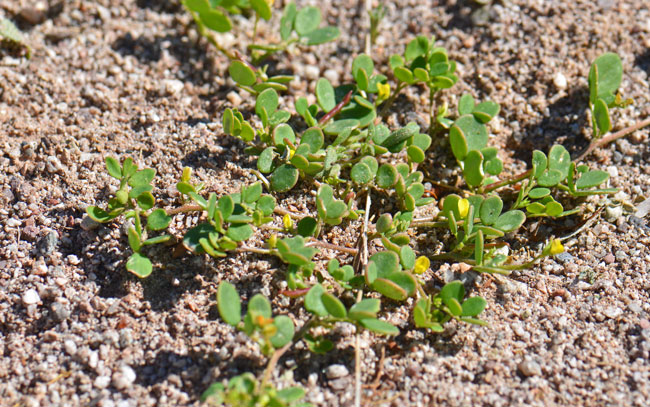
Size: Up to 8 inches ( cm) more or less, a short low-growing herb.
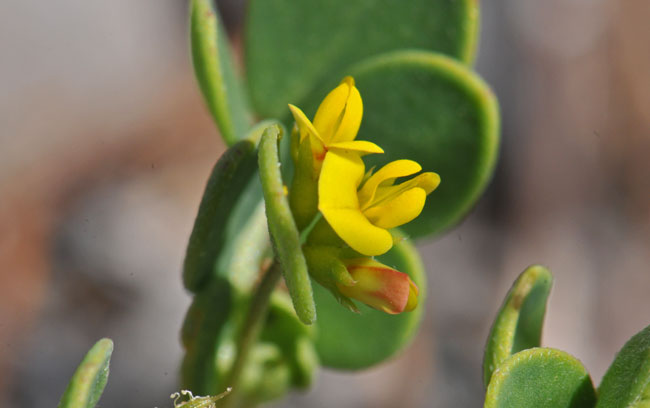
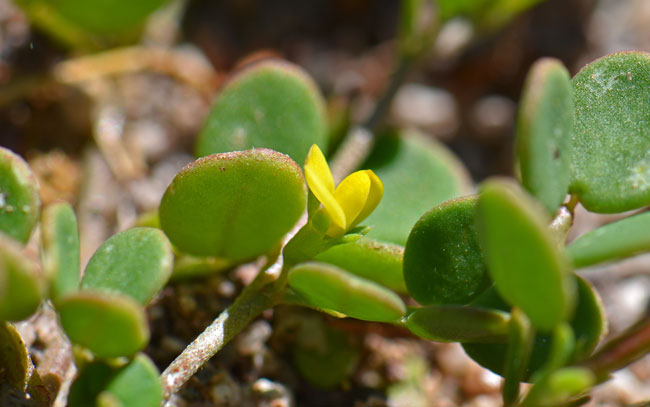
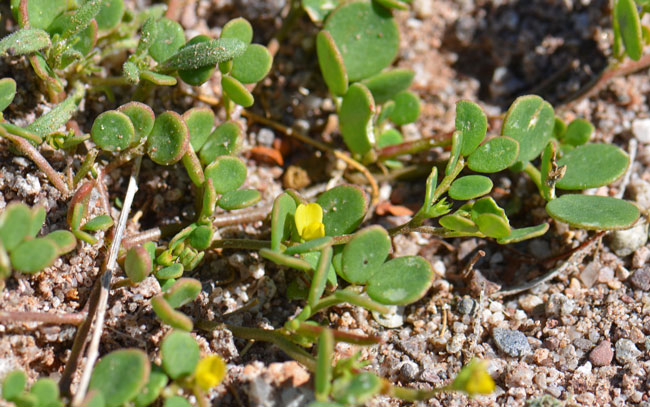
Growth Form: Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil is a forb/herb that is soft and fleshy, the slender stems grow along the ground and then become erect.
Leaves: Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil has soft and fleshy green leaves which line the slender stems in pairs of leaflets of various shapes.
Flower Color: Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil has yellow flowers, the flowering stalks are tipped with 1 to 4 flowers; the fruit is a pod with a hooked beak.
Flowering Season: February to May.
Elevation: 3,000 feet (913 m) or lower, California below 6,000 feet (1,829 m).
Habitat Preferences: Desert areas, mid-level -scrub communities and -woodlands, mountains, mesas, California habitat preferences include coastal scrub, foothill woodlands, washes and deserts. Contrary to its common name, Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil, it does not necessary live near coastal areas.
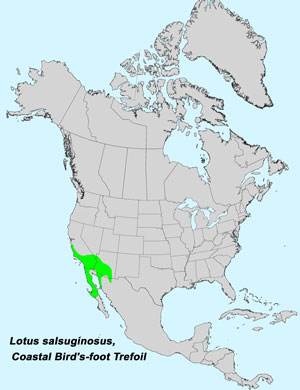
Recorded Range: Lotus salsuginosus is relatively rare in the United States where it is native to the west ½ or AZ, southeast CA and extreme southeast NV. It is also native to Baja California and northern Mexico.
North America & US County Distribution Map for Lotus salsuginosus.
North America species range map for Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil, Lotus salsuginosus:
U.S. Weed Information: Unknown
Invasive/Noxious Weed Information: Unknown
Wetland Indicator: Unknown
Threatened/Endangered Information: Unknown
Genus Information: In North America, USDA Plants Database lists 142 species for Lotus. Worldwide, World Flora Online includes 605 accepted species names for the genus.
The genus Lotus is under current taxonomic review and many species are now classified under the genus Acmispon. Lotus salsuginosus is now also recognized as Acmispon maritimus, Coastal Lotus.The genus Lotus was published in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus, (1707-1778).
In the Southwestern United States: Arizona has 15 species of Lotus, California has 35 species, Nevada has 12 species, New Mexico has 5 species, Texas has 4 species and Utah has 8 species. Data approximate, subject to revision.
There is 1 sub-species and 1 variety in Lotus salsuginosus:Comments: Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil, contrary to its common name does not necessary live near coastal areas. It may be easy to identify with is its often glabrous relatively fleshy thin flat leaflets. The plants and flowers of sub-species "brevivexillus" are smaller than the type species Lotus salsuginosus.
Also see in Southwest Desert Flora; Bird's Foot Trefoil, Lotus corniculatus; Foothill Deervetch, Lotus humistratus; Shrubby Deervetch, Lotus rigidus, and Wright's Deervetch, Lotus wrightii.
It is likely that Lotus salsuginosus evolved under periodic fire events in wildfire-prone habitats such as chaparral, as studies indicate this species has an increased rate of seed germination after exposure to heat.
Also see in Southwest Desert Flora; Bird's Foot Trefoil, Lotus corniculatus; Shrubby Deervetch, Lotus rigidus, Coastal Bird's-foot Trefoil, Lotus salsuginosus and Wright's Deervetch, Lotus wrightii.
The genus Lotus was published in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus, (1707-1778).
The species epithet “salsuginosus” (salsugino'sus:) means growing in places overflowed by salt water, e.g. salt marshes.
The taxon “Lotus salsuginosus” was described in 1890 by Edward Lee Greene, (1843-1915).

