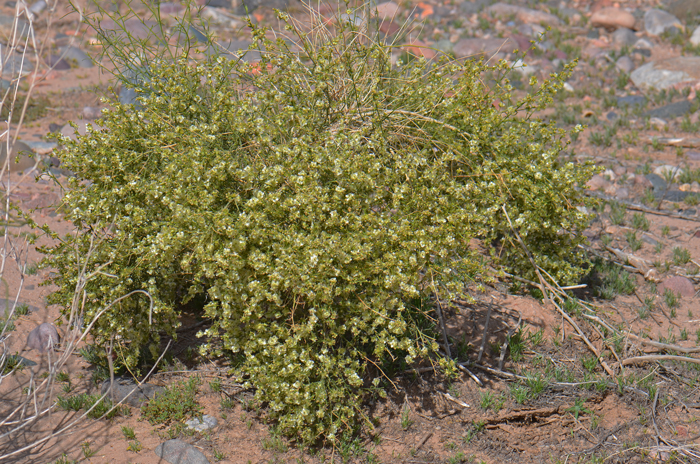
Ambrosia salsola, Cheesebush





Scientific Name: Ambrosia salsola
Common Name: Cheesebush
Also Called: Burrobush, Burrobrush, Desert Pearl, White Burrobrush, White Burrobush, White Ragweed; (Spanish: Jécota).
Family: Asteraceae, Sunflower Family
Synonyms: (Hymenoclea salsola)
Status: Native
Duration: Perennial
Size:Up to 5 feet (150 cm) tall.
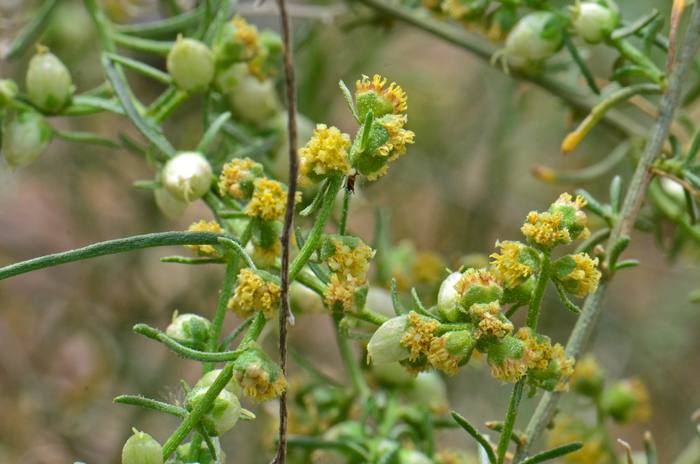
Growth Form: Shrub or subshrub; stems mostly erect; plants rounded but often sprawling habit and straggly; heavy branching throughout, branches relatively thin and/or slender; bark is straw colored (stramineous), striped with parallel, longitudinal lines, ridges or furrows (striate); branches sparsely and finely pubescent
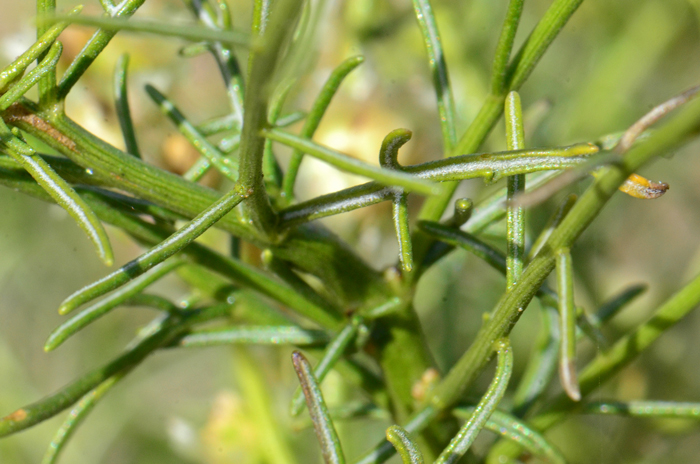
Leaves: Green; alternate along stem; leaf blades thread-like (filiform) and some with 3 to 5 or more filiform-lobes; leaf stems or stalks 0 (sessile); upper side of leaves (adaxial) grooved and covered covered with minutely soft erect whitish hairs (puberulous).
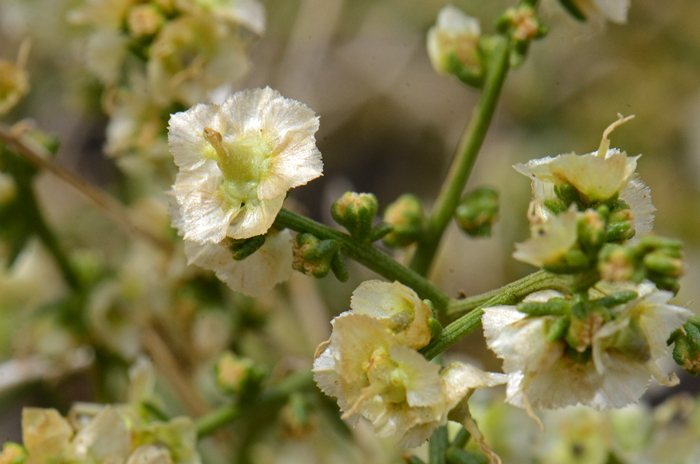
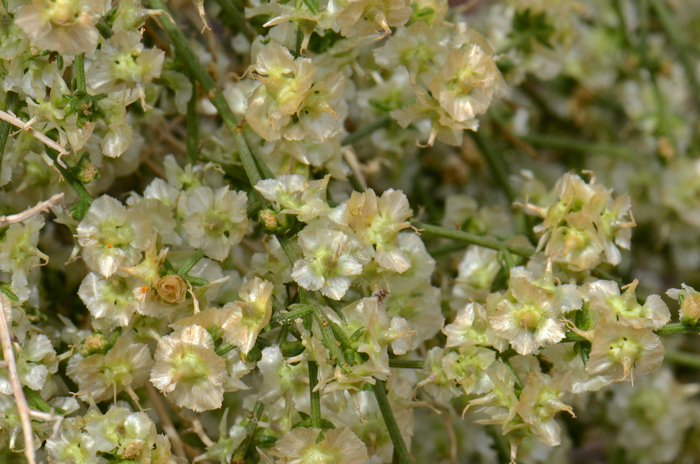
Flower Color: Yellow or white; flowers fade to white or pearly; both male (staminate) and female (pistillate) flowers intermixed on spike-like flowering stalk (inflorescence); flowers profusely in season; fruit a fusiform bur with 7 or more wings.
Flowering Season: March or April to May or June.
Elevation: Up to 6,000 feet (1,800 m)
Habitat Preferences: Sandy or gravelly desert washes and benches, rocky slopes, alkaline soil.
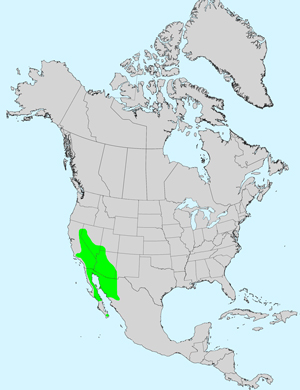
Recorded Range: A southwestern desert plant found in the United States in AZ, CA, NV and the southwest tip of UT and in Baja California and northwest Mexico (Sonora). Found throughout much of Arizona, mostly absent in the northeast part of the state.
North America & US County Distribution Map for Ambrosia salsola (as Hymenoclea salsola).
North America species range map for Ambrosia salsola:
North American range map courtesy of Virginia Tech, Dept. of Forest Resources & Environmental Conservation
U.S. Weed Information: Unknown
Invasive/Noxious Weed Information: Unknown
Wetland Indicator: Unknown
Threatened/Endangered Information: Unknown
The genus Ambrosia was published by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
In the Southwestern United States: Arizona has 15 species of genus, California has 14 species, Nevada and New Mexico each have 8 species, Texas and Utah each have 10 species. Data includes Hymenoclea. All data approximate and subject to revision.
3 varieties of Ambrosia salsola:
Ambrosia salsola var. fasciculata, Burrobush (AZ, CA, NV, UT);
Ambrosia salsola var. pentalepis, Burrobush (AZ, CA, NV);
Ambrosia salsola var. salsola, Burrobush (AZ, CA).
Comments: Cheesebush is a spring bloomer found primarily in sandy or gravelly desert washes generally below 6,000 feet (1,800 m) where it is often a primarily species. It is closely related to Singlewhorl Burrobrush Ambrosia monogyra which blooms in the fall. Pollen from both species causes hay fever in susceptible individuals.
Cheesebush, one of the common names is derived from its foliage which, when crushed has a decidedly cheesy scent. Cheesebush hybridizes with White Bursage Ambrosia dumosa.
Also see in Southwest Desert Flora Canyon Ragweed, Ambrosia ambrosioides, Triangle-leaf Bursage, Ambrosia deltoidea, White Bursage Ambrosia dumosa Hollyleaf Bursage, Ambrosia eriocentra and Singlewhorl Burrobrush Ambrosia monogyra.
Although placed in the Asteraceae family, plants in the genus Ambrosia bear little resemblance to most other members of the daisy family.
The species epithet "salsola" (Salso'la:) is from the Latin salsus for "salty."

