Ambrosia monogyra, Singlewhorl Burrobrush





Scientific Name: Ambrosia monogyra
Common Name: Singlewhorl Burrobrush
Also Called: Burrobrush, Burrobush, Cheeseweed Burrobrush, Needle-Leaf Burrobush, Singlewhorl Burrobush; (Spanish: Jécota, Jejego, Romerillo).
Family: Asteraceae, Sunflower Family
Synonyms: (Hymenoclea monogyra)
Status: Native
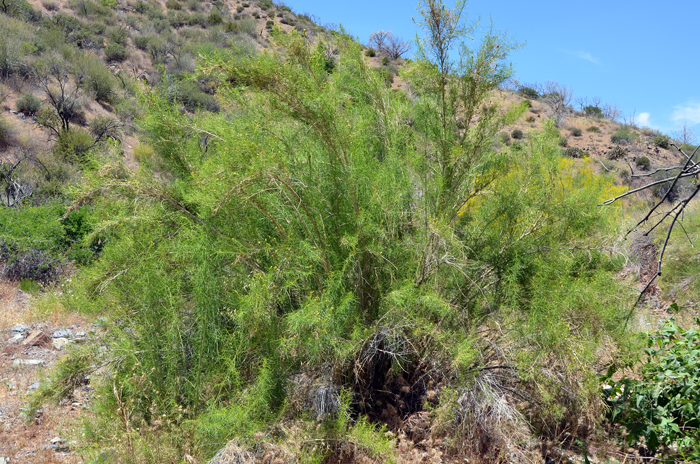
Duration: Perennial.
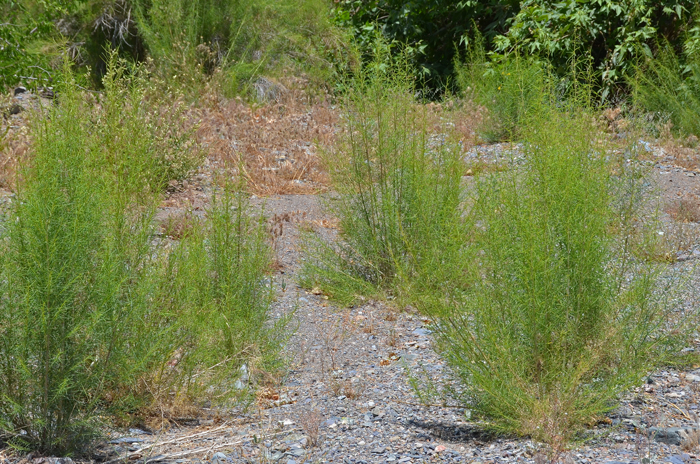
Size: 1 to 5 feet (30-150 cm) tall, or more (12 feet, 370 cm).
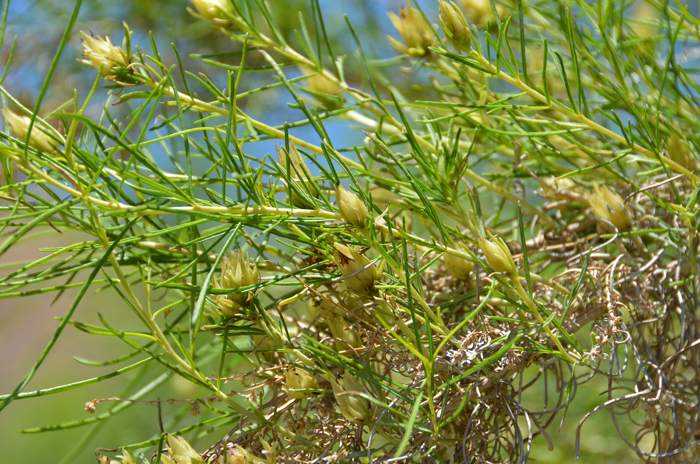
Growth Form: Shrub; plants erect; stems and branches slender, branching above; new stems light green, plants, plants dark brown, brown or straw colored.
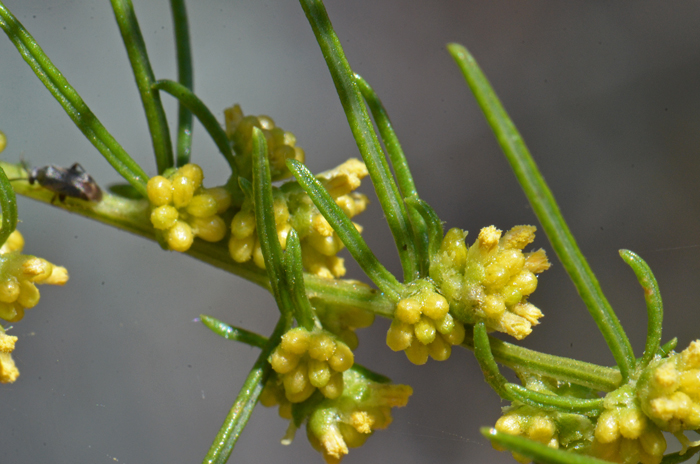
Leaves: Green; alternate along stems; leaves without stem or stalk (sessile); leaves sparse, drought-deciduous; blades filiform, narrow or linear; new leaves may be pinnately divided into segments, or may also be described as having filiform-lobes; lower surface of leaves smooth (glabrous) or becoming smooth (glabrescent), upper surfaces leaves grooved and minutely covered with minute soft white hairs (puberulous)
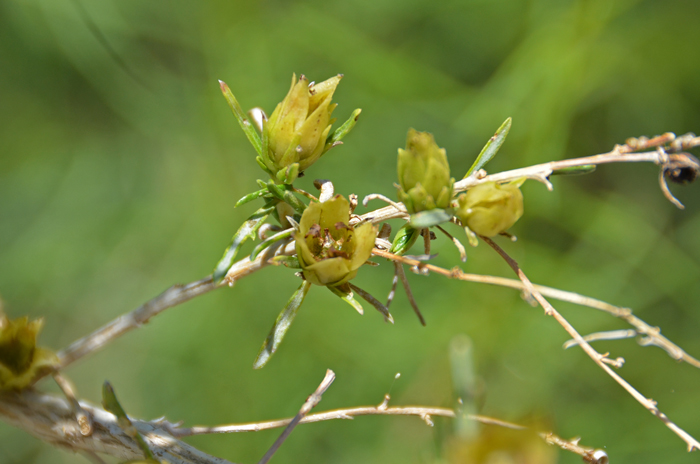
Flower Color: White or green; numerous flowers, male (staminate) and female (pistillate) florets in separate heads, the male flowers have translucent white corollas clustered in leaf axils, the female flowers, also clustered in axils, are rounded fruit-bearing structures; all florets without ray flowers (discoid); female heads 1-flowered; fruit spindle shaped bur with a distinctive whorl of papery bract wings around the middle.
Flowering Season: (May) August or September to October or November
Elevation: 1,000 to 4,000 feet (305-1,200 m); below 1,640 feet (500 m) in California.
Habitat Preferences: Mostly sandy soil, desert washes, ravines, floodplains, and along arroyos.
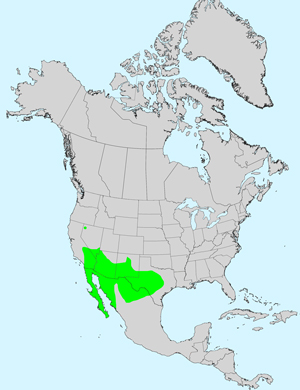
Recorded Range: Singlewhorl Burrobrush is found in the southwest United States in AZ, CA, NM, NV and TX. In the states outside of Arizona it has erratic distribution apparently based on specific habitat requirements. It is marginal in NV. It is also native to Baja California and northwest Mexico (Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Sonora). In Arizona it is locally common where found in the central, southern and western parts of the state.
North America & US County Distribution Map for Ambrosia monogyra (as Hymenoclea monogyra).
North America species range map for Ambrosia monogyra:
North American range map courtesy of Virginia Tech, Dept. of Forest Resources & Environmental Conservation
U.S. Weed Information: Unknown
Invasive/Noxious Weed Information: Unknown
Wetland Indicator: In North America Ambrosia monogyra has the following wetland designations:
Arid West, UPL; Great Plains, FACU; Western Mountains, Valleys, and Coast, UPL.
UPL = Obligate Upland, almost never occur in wetlands;
FACU = Facultative Upland, usually occur in non-wetlands, but may occur in wetlands.
Threatened/Endangered Information: Listed in California as possibly threatened by of trail maintenance and non-native plants.
The genus Ambrosia was published by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
In the Southwestern United States: Arizona has 15 species of genus, California has 14 species, Nevada and New Mexico each have 8 species, Texas and Utah each have 10 species. Data includes Hymenoclea. All data approximate and subject to revision.
Comments: Singlewhorl Burrobrush is a "Burrobrush" that blooms profusely in the fall. It flourishes on disturbance created by occasional floods and its seeds are distributed by flooding.
It is closely related to Cheesebush, Ambrosia salsola which also blooms profusely but in the spring and is much shorter, less than 3 feet (1 m) tall. Pollen from both species causes hay fever in susceptible individuals. A predominate species where found in Arizona however, in California it is listed as threatened because of trail usage and non-native plants. In appearance it is an unlikely member of the daisy family.
Also see in Southwest Desert Flora; Canyon Ragweed, Ambrosia ambrosioides, Triangle-leaf Bursage, Ambrosia deltoidea, White Bursage, Ambrosia dumosa Hollyleaf Bursage, Ambrosia eriocentra, and Cheesebush, Ambrosia salsola.
The species epithet "monogyra" (monogy'ra:) in or with one circle, as in this species which has an inflorescence composed on one central whorl.
See complete species account from Native American Ethnobotany, University of Michigan, Dearborn.

